Defining the Molecular Point of Care (mPOC) Market in 2024
Defining the molecular point of care (mPOC) market is the first step in market-sizing this segment. The mPOC market refers to the use of molecular diagnostic tests at or near the patient’s location to enable rapid and actionable clinical decisions. These tests typically involve the detection of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) from pathogens or genetic markers associated with diseases.
Key characteristics of the mPOC market include:
- DNA or RNA test technology
- Small footprint and reasonably portable
- Result time fast enough for office visit or bedside consultation
- Use possible outside of a reference lab
- Uses cartridges
- Limited or no sample preparation
- Is either running CLIA-waived tests or moderate complexity tests with potential for CLIA-waiver approval.
- While some mPOC systems may be used in labs that find their speed beneficial, that is not always their one purpose.
To establish a market size and forecast for molecular point of care systems, it’s necessary to understand what it is that is being measured. If a market for every dollar earned by selling any system that “could be used” in molecular point of care was established, the market would be much larger and have much more potential growth, possibly. But such a market definition would have little use to the countless new innovators who would like to compete with the likes of GeneXpert, Cobas Liat or BioFire. This is the undertaking of Kalorama Information’s The Market and Future Potential for Molecular Point-of-Care (mPOC), 11th Edition.
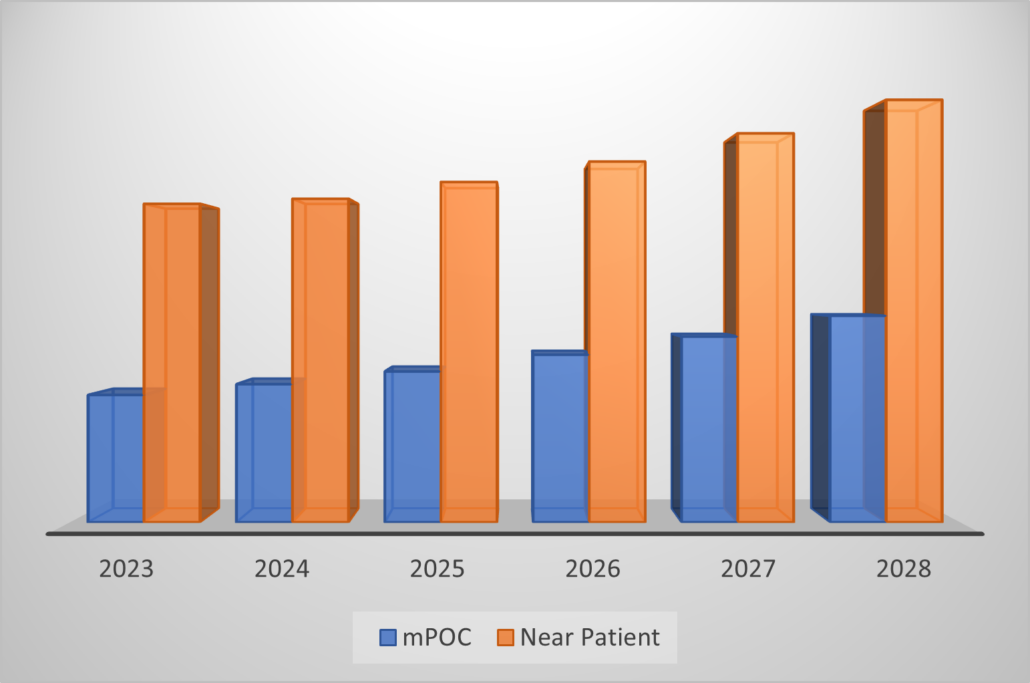
A much larger market can be estimated for molecular systems that can be brought near patient, but which do not meet a true point of care criteria. Near patient molecular systems constitute a multi-billion dollar market segment that more than doubles the mpoc market, however near patient designation includes tests that could be several hours in turnaround and systems that are not usually marketed to physician offices and clinics, and may not have a reasonable chance of a CLIA-waiver in the forecast period. Indeed, near patient is defined as tests with a moderate or high complexity yet performed on a near-patient instrument system, turnaround of several hours, not expected for CLIA-waiver within a five year forecast. Conversely, mPOC tests have a quick turnaround, low operator training, and are CLIA-waived or have a reasonable chance of CLIA waiver in the near term.
Molecular point of care testing is also known as near-patient testing, or rapid PCR testing. POC diagnostics are preferred in certain episodes of care for shorter turnaround time or time to results when care implementation or triage is needed rapidly. The usability features of POC tests help enable rapid performance, but also expand their applicability across care settings. Key features of POC tests, including molecular POC tests, include simple results interpretation and integration of test procedures that minimize hands-on time and risk of user error. In low-healthcare resource areas of the developing world, POC tests are often preferred as they can be completed outside of laboratory settings, without lab infrastructure that is often difficult to access, and they can be conducted by people with little to no laboratory training. Lastly, POC tests find some preferential use in healthcare as a source of billing revenue otherwise claimed by independent labs.
Examples of POC settings include the following:
- Decentralized hospital labs or testing points found in emergency departments (ED), operating rooms (OR), intensive care units (ICUs) and other patient wards or hospital departments
- Bedside in a hospital using a portable device
- Labs or testing workstations at physician offices, physician practices or outpatient clinics such as rural health clinics, community clinics, public health clinics, student health clinics, sexual health clinics, retail clinics and other specialty clinics
- Small hospitals, community health posts, mobile clinics and field screening sites in the developing world without access to clinical lab infrastructure and where screening and other testing is performed largely with POCT products
- Ambulatory surgery centers
- Pharmacies
- Nursing home, hospice care center, long-term care facility, or even In-home or within the patient residence (performed by the patient or visiting medical professional)
- Workplace
- Military locations
- Mobile Laboratories and clinics
Looking ahead, Kalorama forecasts that both mPOC and near patient systems will have a roughly 6% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2023-2028.
Trends driving growth in the mPOC market t include:
- Collaborations, Acquisitions
- Supportive mPOC Studies
- Menu Expansion
- Product Launches
- PAMA Impact
- Uptick in Investment in mPOC Companies
- China POC Market
- Raman Spectroscopy
- Emerging Markets
- Coronavirus
- Competitive Immunoassay Products
For more information, purchase The Market and Future Potential for Molecular Point-of-Care (mPOC), 11th Edition.
About Kalorama Information
Kalorama Information, part of Science and Medicine Group, is the leading publisher of market research in healthcare areas, including in vitro diagnostics (IVD), biotechnology, medical devices, and pharmaceuticals. Kalorama Information produces dozens of reports a year. The firm offers a Knowledge Center, which provides access to all published reports.
Kalorama Information’s studies feature independent primary research conducted by experienced analysts. Researchers build their market analysis independently from published databases, validating data with inside industry contacts and extensive secondary research, so you can have confidence that you’re getting your information from the most trusted source in the industry!